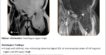
LEIGH’S SYNDROME
Clinical information: Abnormal behavior and difficulty in speaking.
Findings:
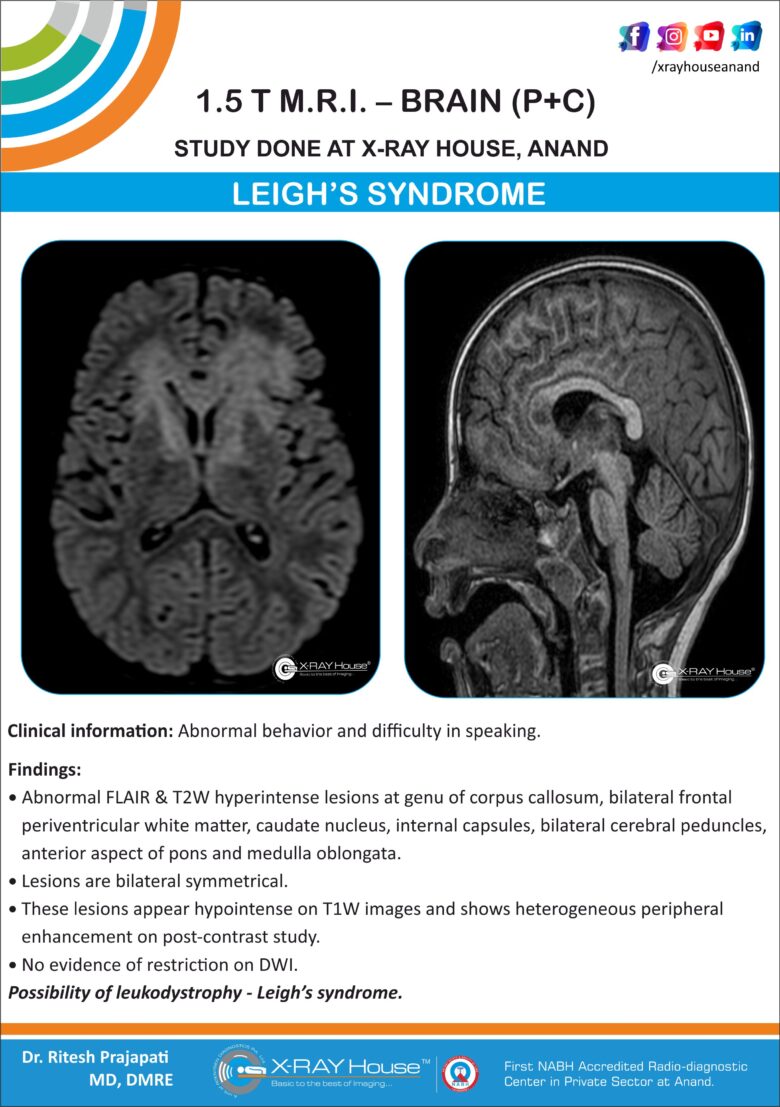
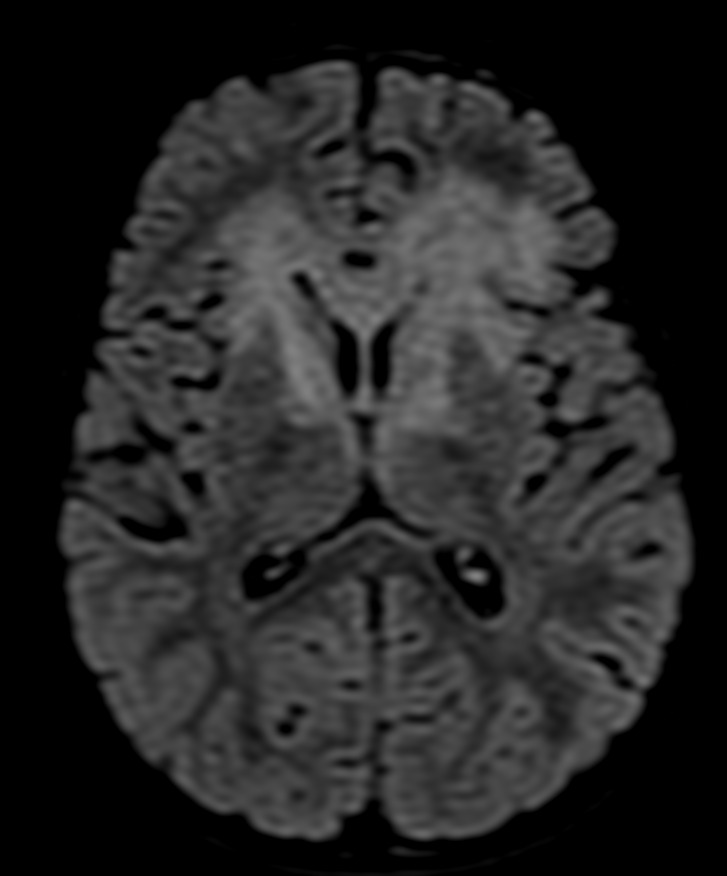
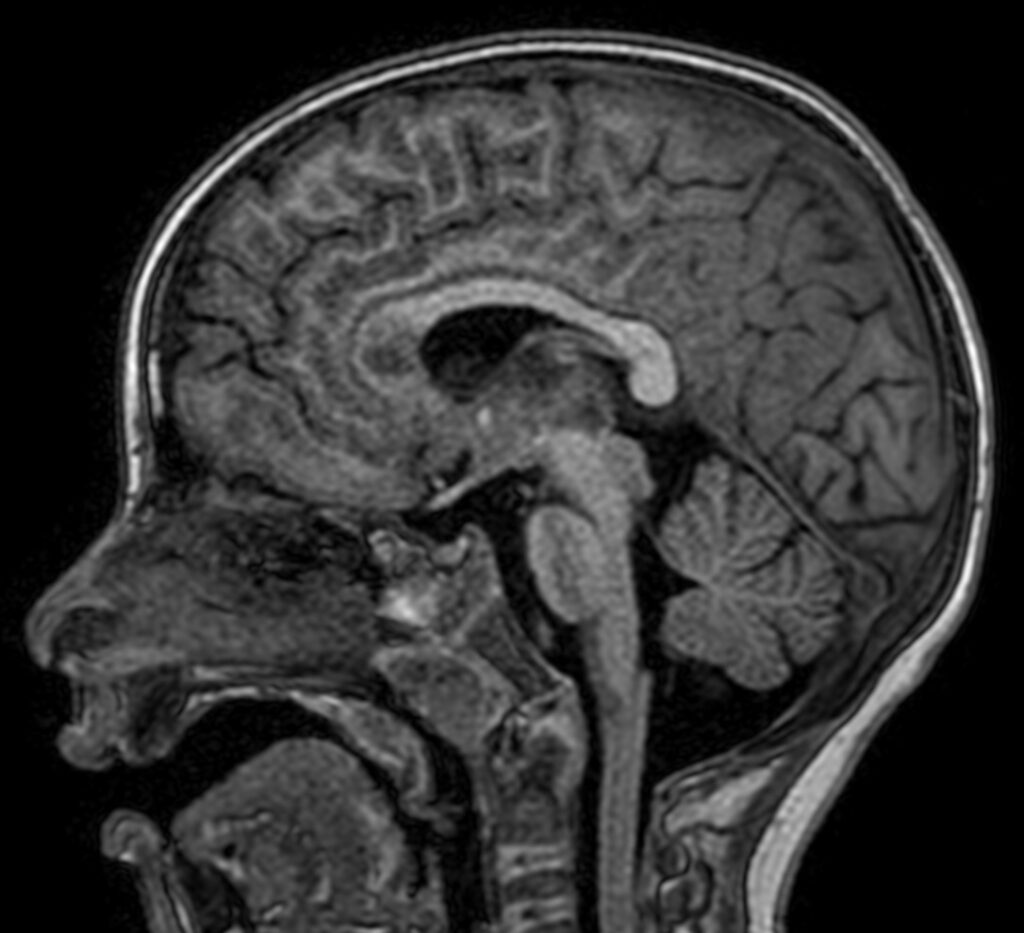
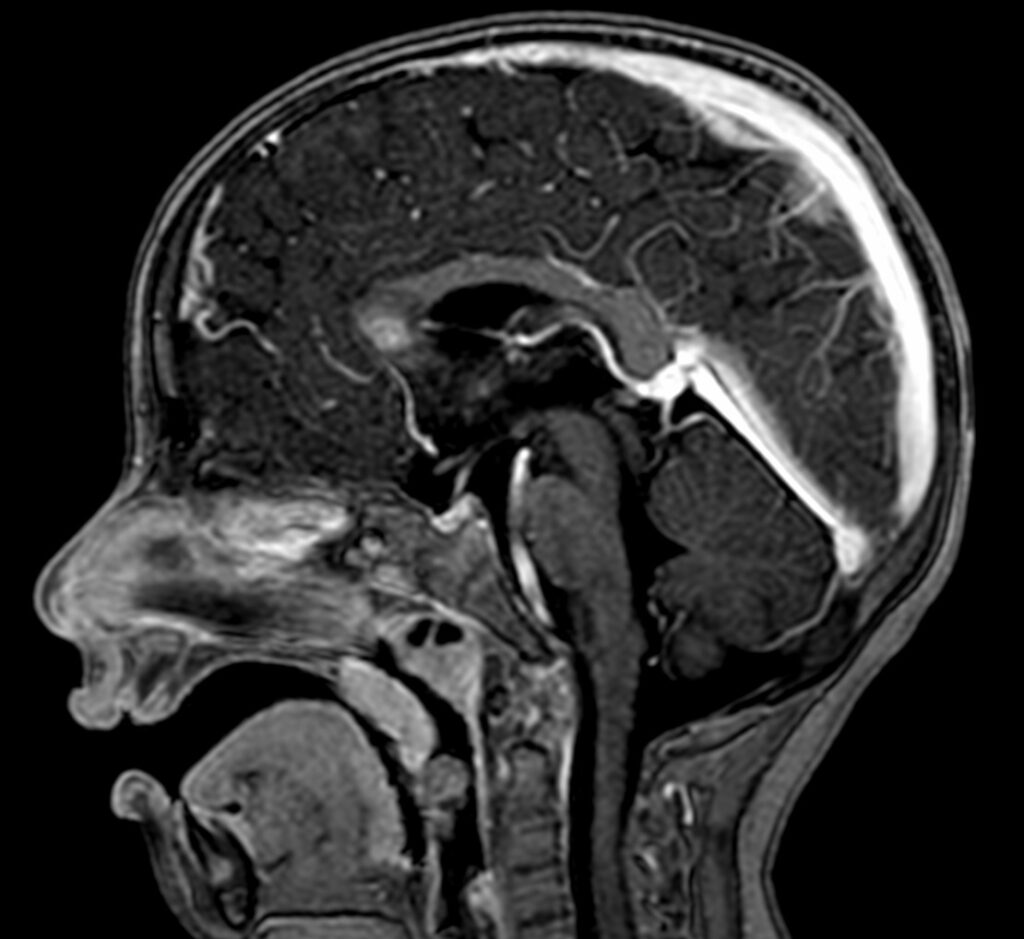
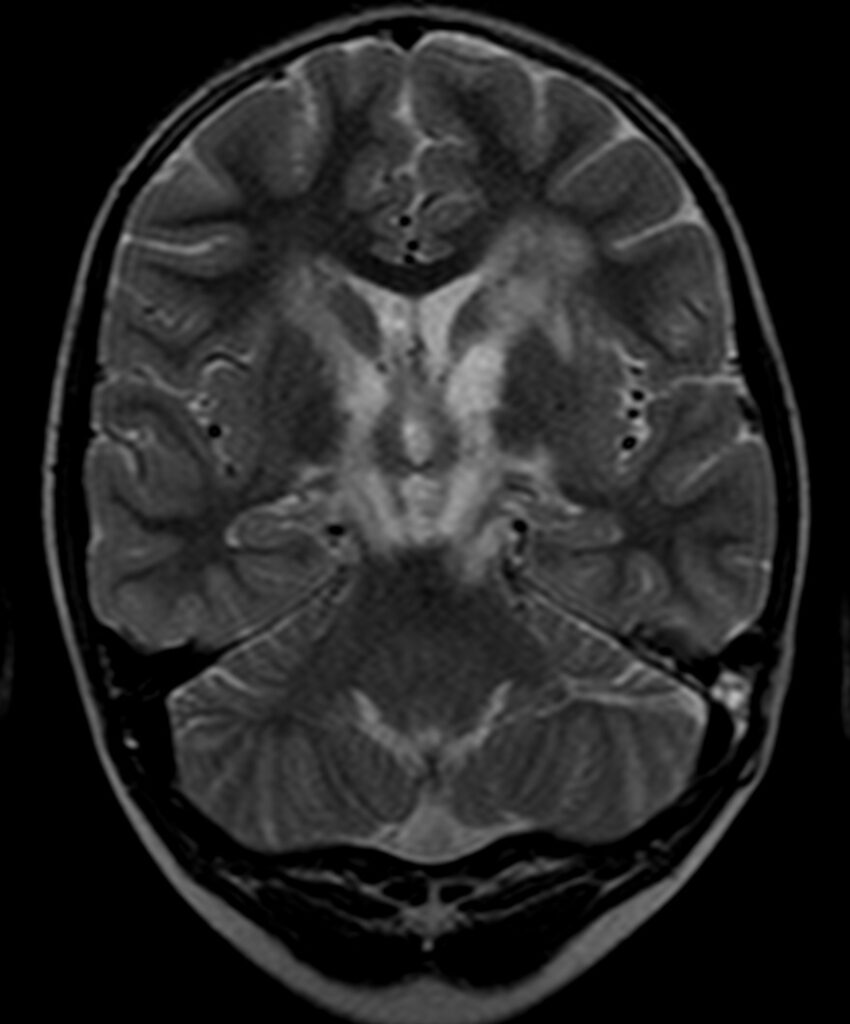
Abnormal FLAIR & T2W hyperintense lesions at genu of corpus callosum, bilateral frontal periventricular white matter, caudate nucleus, internal capsules, bilateral cerebral peduncles, anterior aspect of pons and medulla oblongata.
Lesions are bilateral symmetrical.
These lesions appear hypointense on T1W images and shows heterogeneous peripheral enhancement on post-contrast study.
No evidence of restriction on DWI.
Possibility of leukodystrophy – Leigh’s syndrome.
DISCUSSOIN:
- Leigh syndrome is a rare and severe neurometabolic disorder. With neurometabolic disorders, the nervous system does not work properly.
- Leigh syndrome is a type of primary mitochondrial disease.
- This condition primarily affects babies and young children. Symptoms usually start between the ages of three months and two years. It can also occur in teenagers and adults. However, this is less common.
- Leigh syndrome affects at least 1 in 40,000 people.
- The disease is progressive. It is likely to gradually worsen over time.
- Patients with Leigh syndrome have specific brain lesions. The presence of these lesions is key to diagnosis. These lesions typically appear in certain brain structures. This includes:
- The basal ganglia
- The brainstem
Article Tags:
1.5T · MRI
Article Categories:
1.5 MRI
Likes:
0