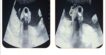
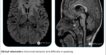
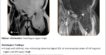
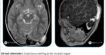
The best imaging modality for the diagnosis of myxopapillary ependymoma is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) because of its superior soft-tissue contrast. MRI is helpful in identifying the extent of the tumor and its relationship to intraspinal structures.
Clinical History: A Patient presented with complains of lower back pain.
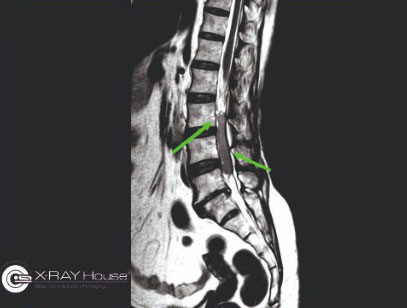
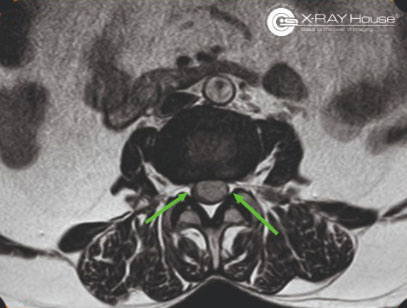
RADIOLOGICAL FINDINGS:
Findings are suggestive of homogeneously enhancing intradural neoplastic lesion in the spinal canal at L2 to L4 levels
- possibility of filum terminale myxopapillary ependymoma.
Article Tags:
L.S.SPINE
Article Categories:
3.0 MRI · CT SCAN
Likes:
0