CARDIAC MRI
FINDINGS:
- Normal sized left ventricle showing normal systolic function.
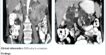
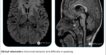
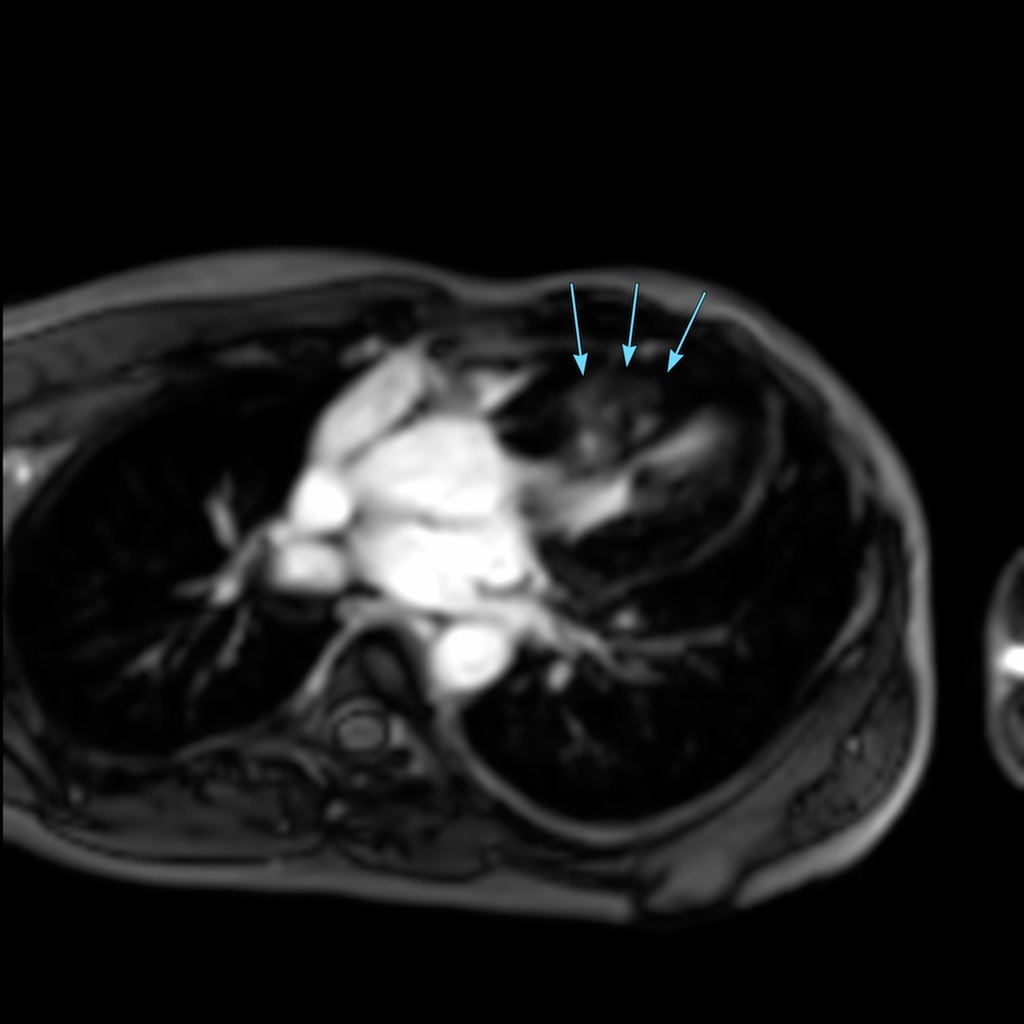
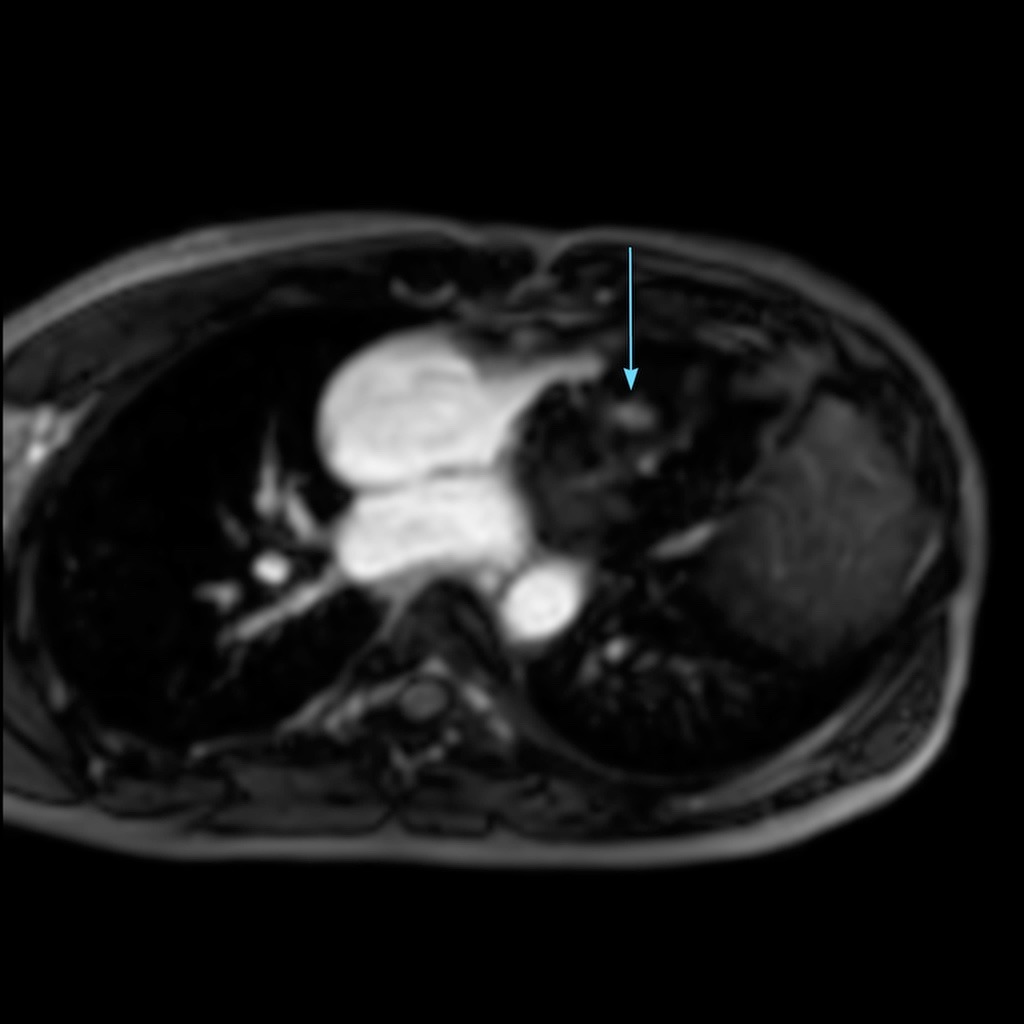
- Severe asymmetric hypertrophy of the basal anterior, basal antero-septal, basal infero-septal, basal inferior, mid antero-septal, mid infero-septal and mid inferior segments; and Moderate asymmetric hypertrophy of mid anterior, mid antero-lateral and mid infero-lateral segments of left ventricle.
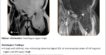
- Diffuse mid-myocardial & sub-epicardial late gadolinium enhancement with subtle myocardial edema involving the hypertrophied segments of left ventricle, maximum in the mid antero-lateral segment.
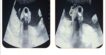
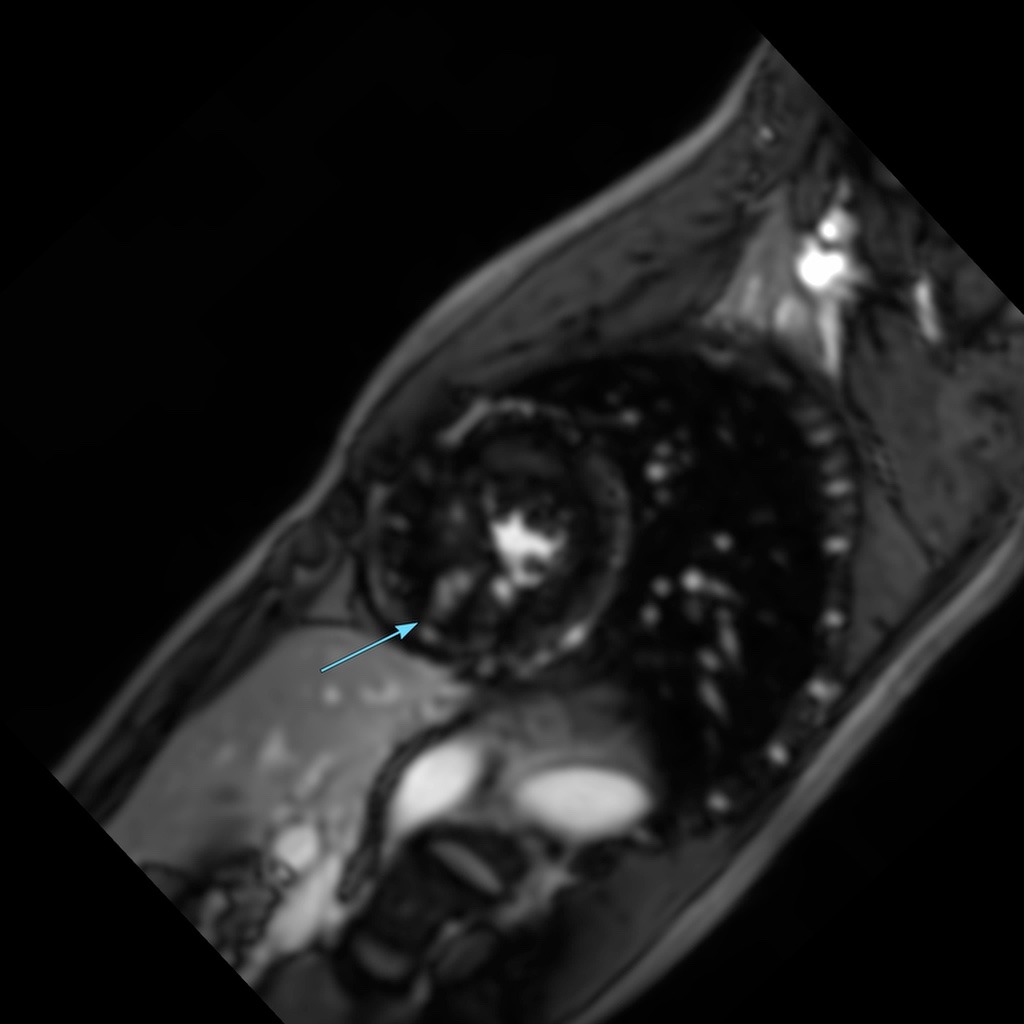
- Grade IV SAM at rest; Systolic anterior motion of anterior mitral valve leaflet at rest with the tip of the anterior mitral valve leaflet abutting the basal interventricular septum,
- Dynamic obstruction of Left Ventricular Outflow Tract at rest.
Features s/o Asymmetric hypertrophy with mid-ventricular variant of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy.
High risk factors for sudden cardiac death include
- Maximum End-Diastolic Wall Thickness of 30.1 mm.
- Myocardial Scar Percentage of 20 % (more than 15%)
- Grade IV SAM with dynamic LVOT obstruction at rest
DISCUSSION:
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is characterized by a hypertrophied left ventricle without any identifiable cause such as hypertension or valvular disease.
- There is asymmetric thickening of the wall most prominently involving the ventricular septum.
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is the most common monogenic cardiovascular disorder. It is most common cause of sudden death in young athletes.
- In about 25% of patients there is obstruction of the left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) due to hypertrophy of the basal septum and a systolic anterior motion of the mitral valve (SAM).
- In these cases the term HOCM or hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy is used.
- Imaging is fundamental for diagnosis, characterization, and risk stratification and to guide therapy. Echocardiography is the initial imaging modality for evaluation of cardiac morphology.
- Cardiac MR imaging is a powerful tool that provides clinically useful information for screening, accurate diagnosis, and determination of clinical management strategies.
- Detection & quantification of scar & fibrosis using the delayed enhancement technique is it’s unique ability.
- Cardiac CT is alternative modality in when cardiac MR imaging is contraindicated.
Article Categories:
1.5 MRI · 3.0 MRI · Case Study
Likes:
0