PLAIN CT SCAN OF BRAIN
FINDINGS:
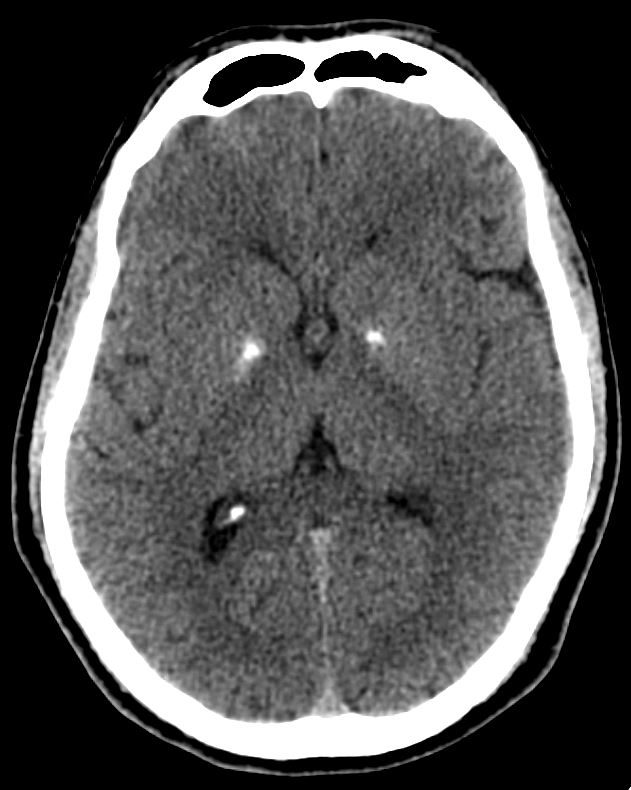
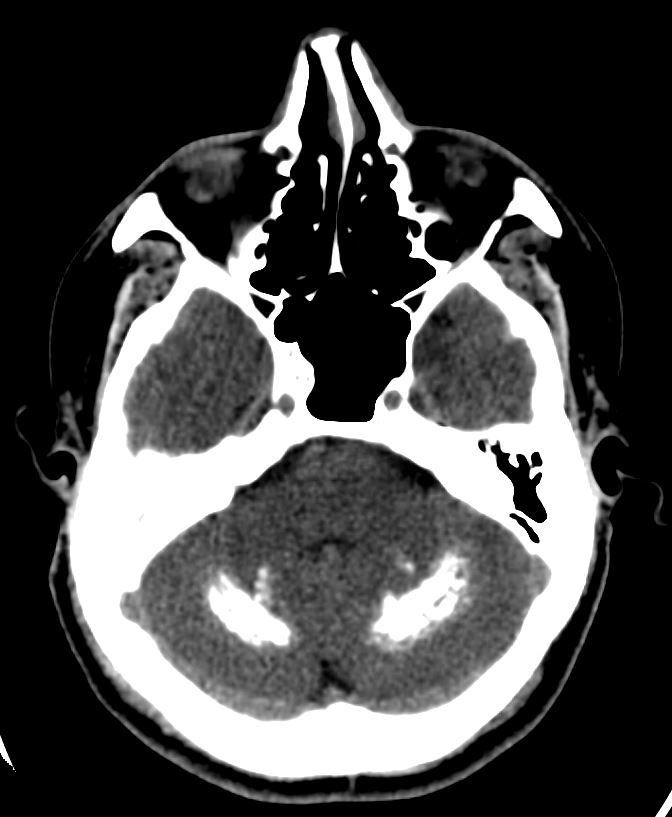
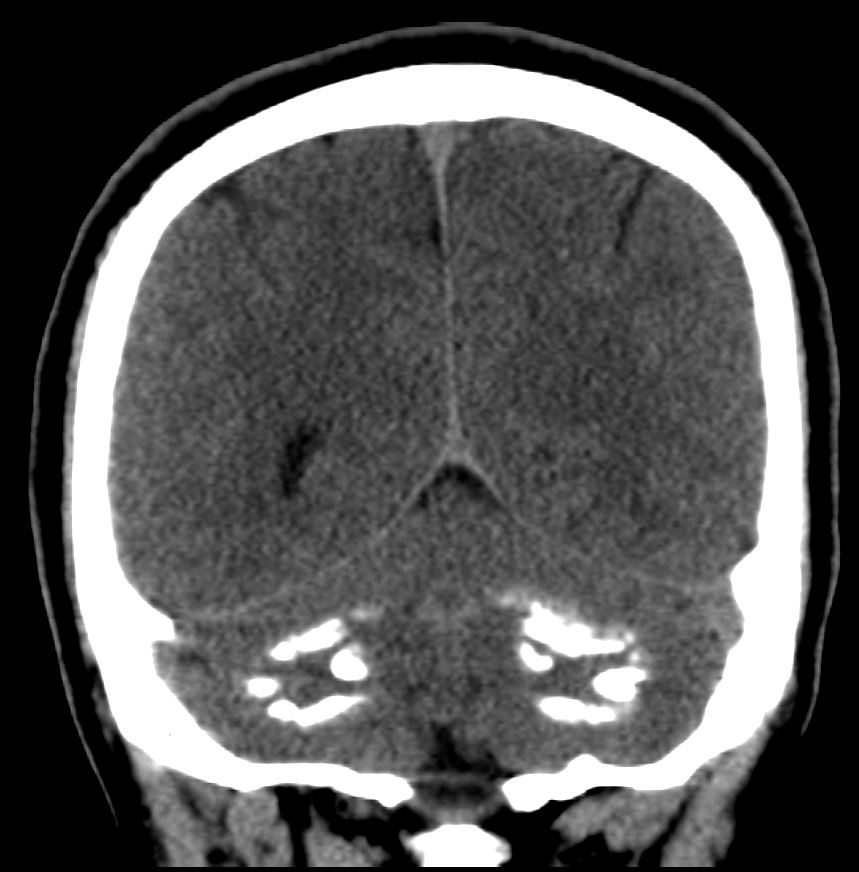
- Evidence of bilaterally, symmetrical hyperdensities are noted at basal ganglia and cerebellar hemispheres – represents a foci of calcifications.
Features suggests possibility of Fahr’s disease.
DISCUSSION:
- Fahr syndrome, also known as bilateral striatopallidodentate calcinosis.
- It is a genetically dominant, degenerative disorder characterized, clinically by multiple neurological and psychiatric symptoms occurring secondary to calcification in brain parenchyma with subsequent neuronal loss.
- Presence of bilateral and symmetrical intra-cerebral calcifications in the basal ganglia, thalamus, dentate nucleus and centrum semiovale region due to unknown aetiology is referred to as Fahr’s disease or idiopathic striopallidodentate calcinosis.
- Fahr’s syndrome includes Fahr’s disease as well as secondary causes of striopallidodentate calcinosis.
- The calcifications are bilateral and symmetric, extensive, irregular, amorphous, intraparenchymal calcifications, these calcium deposits consist of calcium carbonate and calcium phosphate.
- Fahr syndrome, which generally refers to secondary causes, has been associated with a large number of conditions, most common of which are endocrinopathies, mitochondrial disorders, and infectious diseases.
- In all cases of suspected Fahr syndrome, additional tests should be performed to investigate for a potential secondary cause, and exclude other differential diagnoses.
- The clinical presentation is variable, with many individuals remaining asymptomatic. The most common neurological manifestations include headache, seizures and movement disorders. Other specific manifestations include gait disturbances, dystonia, paresis, speech alterations, dementia, Parkinsonism, tremors, chorea.
- Fahr syndrome is typically diagnosed in younger individuals when a secondary cause is identified with appropriate intracranial imaging features.
- T2 GRE magnetic resonance images (MRI) are sensitive for calcifications as areas of low signal.
- However, Brain CT scan: Most sensitive modality in localizing and assessing the extent of Cerebral Calcifications.
Article Categories:
CT SCAN
Likes:
0