Supra-Cardiac Partial Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Drainage (PAPVC / D).
FINDINGS:
Systemic Veins:
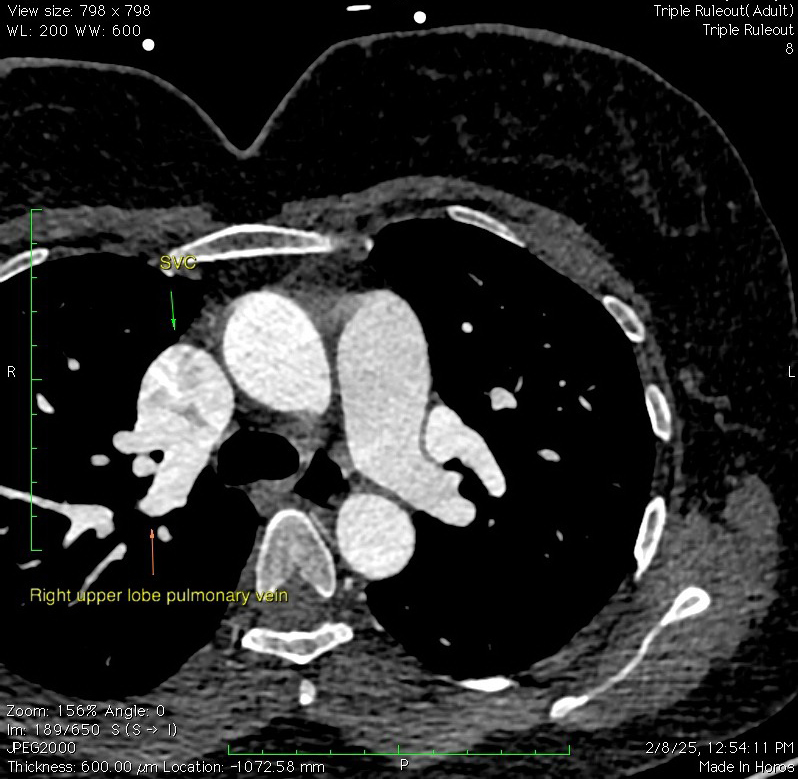
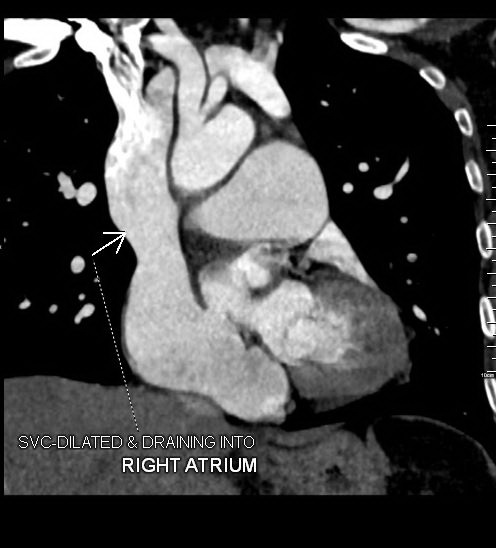
SVC: Single right sided SVC is seen.
The SVC is dilated and is seen draining into the right atrium.
Right Atrium: Right atrium is dilated.
Right Ventricle: The right ventricle is dilated. Mild right ventricular wall & trabecular hypertrophy is seen.
Pulmonary arteries: The pulmonary arteries are dilated.
No evidence of intraluminal filling defect is seen in the pulmonary arteries.
Pulmonary Veins:
The right upper lobe pulmonary veins are seen draining, through 3 separate veins, into the SVC just inferior to the level of SVC – azygous vein junction; measuring 6 mm, 6.5 mm and 9.9 mm from antero-inferior (8 o’clock) to postero-superior (6 o’clock).
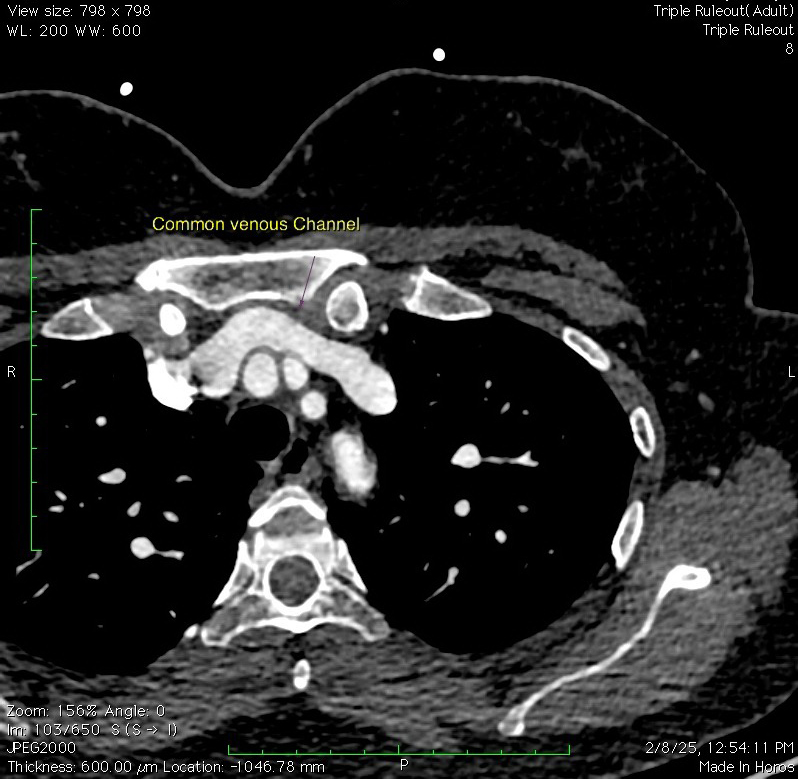
The pulmonary veins of left upper lobe & lingula form a common venous channel measuring ~ 12.4 x 11.7 mm in diameter which drains into the left brachiocephalic vein.
The pulmonary veins of right middle lobe, right lower lobe & left lower lobe are seen draining into to left atrium.
Congenital heart disease – Supra-Cardiac Partial Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Drainage (PAPVC / D).
Changes of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH).
Discussion:
Partial anomalous pulmonary venous return (PAPVR), also known as partial anomalous pulmonary venous connection (PAPVC), is a rare congenital cardiovascular condition in which some of the pulmonary veins, but not all, drain into the right heart or systemic venous system, rather than in the left atrium.
The overall prevalence of PAPVR is 0.4-0.7% 9.
Patients with large shunts may present with symptoms of dyspnea, chest pain and palpitations, signs like tachycardia and murmur can be encountered.
Four types of PAPVR have been described:
- supra-cardiac, 2) cardiac 3) infracardiac 4) mixed.
CT angiography of the aorta is the investigation of choice, as it is used not just for diagnosis and classification but also to rule out any complications.