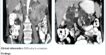
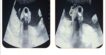
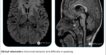
DIAPHRAGMATIC HERNIA
HIGH RESOLUTION C.T. SCAN OF CHEST
Clinical information: Cough and breathing difficulty.
⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯
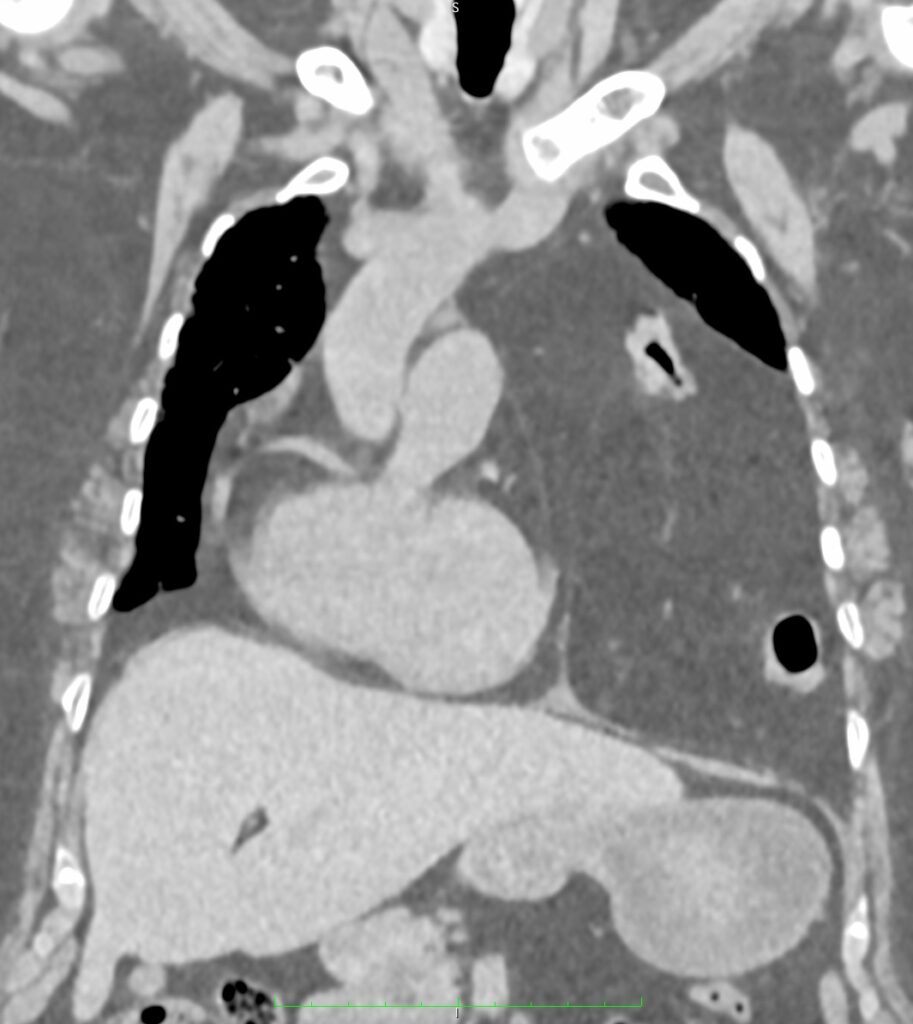
Findings:
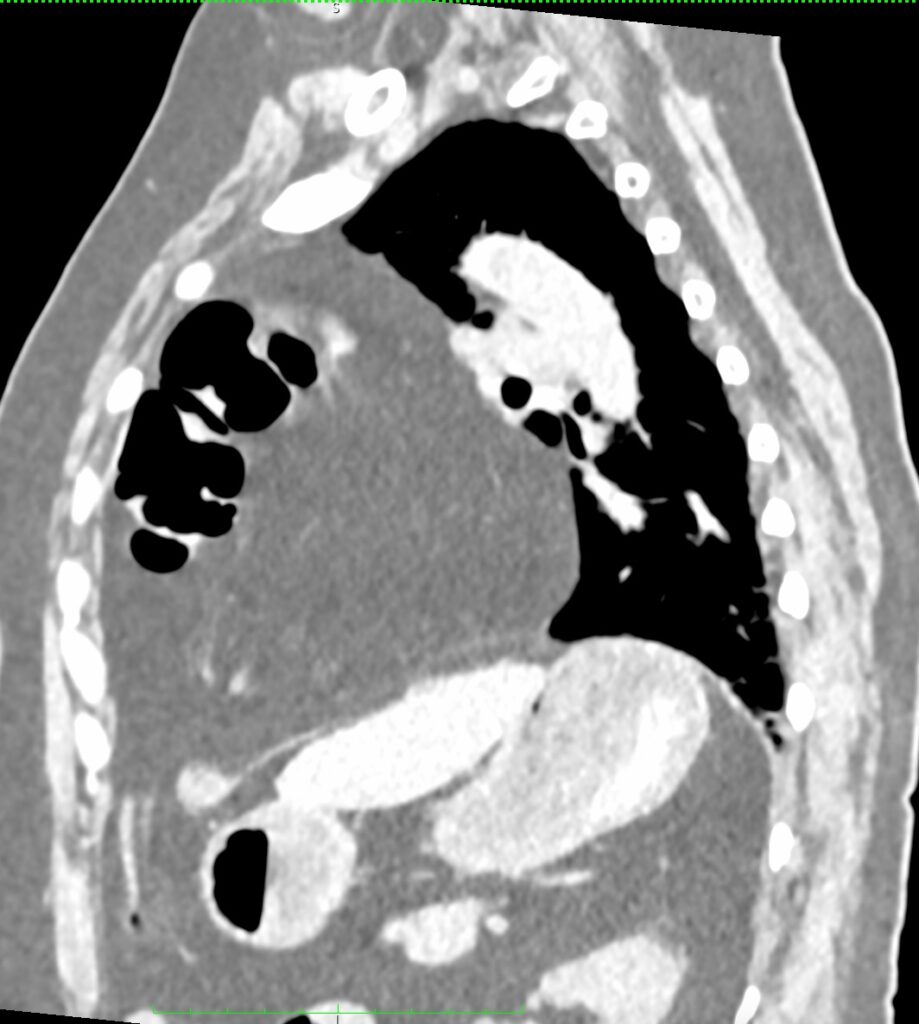
➡ A large defect noted at anterior aspect of diaphragm.
➡ Resultant intrathoracic herniation of omental and peritoneal fat and vessels as well as distal transverse colon, splenic flexure of colon and proximal descending colon.
➡ Herniated abdominal contents are predominantly located in left hemithorax and reaches up to the level of manubrium sterni.
➡ There is resultant shifting of mediastinum toward right side.
Discussion:
➡ A diaphragmatic hernia (Diaphragmatic Hernia) is a protrusion of abdominal contents into the thoracic cavity due to a defect within the diaphragm. It is most common as a congenital phenomenon; however, it can also be acquired.
➡ Most commonly, acquired diaphragmatic hernia occurs following blunt or penetrating trauma, which results in a rupture of the diaphragm and herniation of abdominal contents.
➡ Additionally, acquired diaphragmatic hernia can also occur spontaneously or by iatrogenic causes.
➡ CT scan is modality of choice to detect diaphragmatic hernia. Contents of hernial sac as well as any complications like bowel strangulation or gangrene can be detected by CT scan.